Solar Panel
Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic (PV) panels, are devices that convert sunlight into electricity. They are made up of many solar cells, which are typically made from silicon, a semiconductor material. When sunlight hits these cells, it excites electrons, creating an electric current. Here are some key points about solar panels:
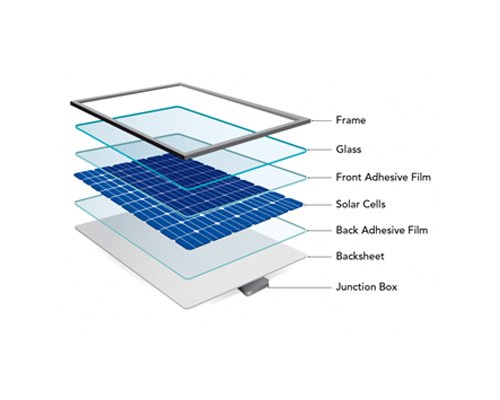
- Composition: Solar panels are made of individual solar cells, which are connected together to form a module. These modules are then connected to form a solar panel.
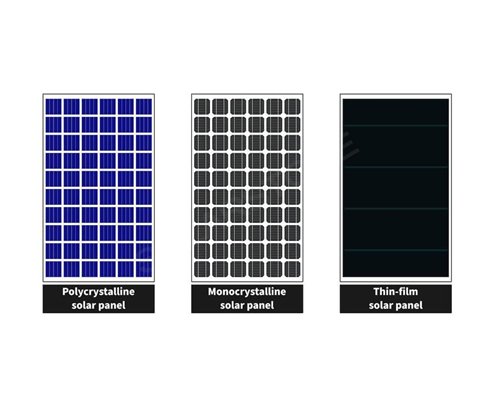
- Types of Solar Panels: There are different types of solar panels, including monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film. Monocrystalline panels are made from single-crystal silicon and are known for their high efficiency. Polycrystalline panels are made from multiple silicon crystals and are slightly less efficient but more affordable. Thin-film panels use layers of photovoltaic material deposited onto a substrate and are often more flexible and lightweight.
- Efficiency: The efficiency of a solar panel refers to the percentage of sunlight that it converts into electricity. Higher efficiency panels can generate more electricity in the same amount of space, but they are often more expensive.
- Installation: Solar panels are typically installed on rooftops or in open areas where they can receive direct sunlight. The angle and orientation of the panels can affect their efficiency, so they are usually installed facing south in the northern hemisphere and north in the southern hemisphere.
- Inverter: The electricity generated by solar panels is direct current (DC), but most household appliances use alternating current (AC). Therefore, solar panels are connected to an inverter, which converts the DC electricity into AC electricity that can be used in homes or fed back into the grid.
- Maintenance: Solar panels require little maintenance, but they should be cleaned periodically to remove dirt and debris that can reduce their efficiency. They also may need occasional inspection for any damage or defects.
- Environmental Benefits: Solar panels produce electricity without emitting greenhouse gases or other pollutants, making them a clean and renewable energy source. They can help reduce dependence on fossil fuels and mitigate climate change.
- Cost: The cost of solar panels has decreased significantly in recent years, making them more accessible to homeowners and businesses. Additionally, there are often financial incentives and rebates available for installing solar panels, which can help offset the initial investment.
Overall, solar panels offer a sustainable and environmentally friendly way to generate electricity, and their popularity continues to grow as technology advances and costs decrease.